Threaded Fittings general
Threaded joints probably represent the oldest method of joining piping systems. Like Socket Weld fittings, threaded fittings are mainly used for small pipe diameters (Small Bore Piping); generally for piping whose nominal diameter is NPS 2 or smaller.
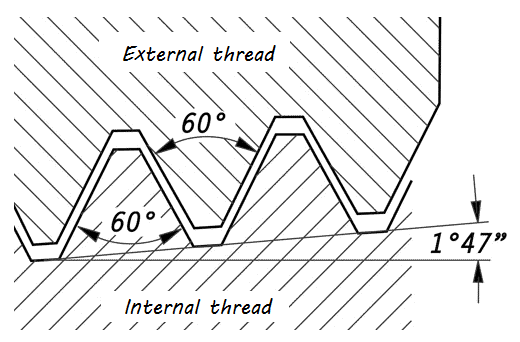
The dimensional standards for taper pipe threads are given in ASME B1.20.1. That document gives all required dimensions including number of threads per inch, pitch diameter, and normal engagement lengths for all pipe diameters.
- Threaded piping is commonly used in low-cost, noncritical applications such as domestic water, fire protection, and industrial cooling water systems.
- Threaded fittings are normally made of cast gray or malleable iron, cast brass or bronze, or forged alloy and carbon steel.
- They are available in three pressure ratings: Class 2000, 3000 and 6000.
NPT Thread
All fittings on this page are described, are provided with NPT thread, ASME B1.20.1. The American National Pipe Thread Tapered, is the best known and most widely used connection where the pipe thread provides both the mechanical joint and the hydraulic seal. NPT has a tapered male and female thread which seals with Teflon® tape or jointing compound.
DIMENSIONS OF AMERICAN TAPER PIPE THREAD, WITH SEALANT COMPOUND
DN-NPT | Major Diameter | Tapping | TPI | Pitch |
1/16" | 7.895 | 6.00 | 27 | 0.941 |
1/8" | 10.242 | 8.25 | 27 | 0.941 |
1/4" | 13.616 | 10.70 | 18 | 1.411 |
3/8" | 17.055 | 14.10 | 18 | 1.411 |
1/2" | 21.223 | 17.40 | 14 | 1.814 |
3/4" | 26.568 | 22.60 | 14 | 1.814 |
1" | 33.228 | 28.50 | 11.5 | 2.209 |
1¼" | 41.985 | 37.00 | 11.5 | 2.209 |
1½" | 48.054 | 43.50 | 11.5 | 2.209 |
2" | 60.092 | 55.00 | 11.5 | 2.209 |
2½" | 72.699 | 65.50 | 8 | 3.175 |
3" | 88.608 | 81.50 | 8 | 3.175 |
3½" | 101.316 | 94.30 | 8 | 3.175 |
4" | 113.973 | 107.00 | 8 | 3.175 |
5" | 141.300 | 134.384 | 8 | 3.175 |
6" | 168.275 | 161.191 | 8 | 3.175 |
8" | 219.075 | 211.673 | 8 | 3.175 |
10" | 273.050 | 265.311 | 8 | 3.175 |
12" | 323.850 | 315.793 | 8 | 3.175 |
TYPES OF THREADED FITTINGS BY CLASS AND SIZE
Description | Class Designation | ||
2000 | 3000 | 6000 | |
Elbows 45 and 90 degrees | 1/2 - 4 | 1/2 - 2 | 1/2 - 2 |
1/2 - 4 | 1/2 - 2 | 1/2 - 2 | |
1/2 - 4 | 1/2 - 2 | 1/2 - 2 | |
Pipe Wall | SCH 80 / XS | SCH 160 | XXS |
Fittings for Threaded Pipe systems
| |
ELBOW 90° | TEE |
| |
CROSS | ELBOW 45° |
| |
FULL-COUPLING | CAP (END CAP) |
| |
HALF-COUPLING | SQUARE HEAD PLUG |
| |
HEX HEAD PLUG | ROUND HEAD PLUG |
| |
HEX HEAD BUSHING | UNION (MSS SP-83) |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Threaded Fittings
ADVANTAGES
- Installation productivity is moderately high, and specialized installation skill requirements are not extensive.
- Leakage integrity is good for low-pressure, low-temperature installations where vibration is not encountered.
DISADVANTAGES
- Rapid temperature changes may lead to leaks due to differential thermal expansion between the pipe and fittings.
- Vibration can result in fatigue failures of screwed pipe joints due to the high stress intensification effects caused by the sharp notches at the base of the threads.
- In hazardous piping systems threaded connections should be avoided, if possible. Their vulnerability to fatigue damage is significant, especially where exposed threads are subject to corrosion.














